
What is RAYDENT technology?
What is RAYDENT technology?
The RAYDENT diffused amorphous coating is a very thin film. It has very high rust inhibiting power and very high adhesion to many organic polymer materials. It also has very high accuracy. These properties are used in metallic surface improving design methods. As a next-generation surface engineering system, it is currently used for semiconductor and liquid crystal packaging FA and the like. It enjoys an overwhelmingly good reputation in the area of electronic and optical precision equipment and plays a leading role in the industry. This technology was originated by Ken Ogawa, Kyoto Prefecture, in 1964 and is an entirely original technology of Japan. In addition, it opened new frontiers for Faraday’s 19-century law of electrolysis. It may said to be a historical monument whose demonstration has taken 30-odd years.
Magnified view of RAYDENT coating

Three-dimensional fine cracks develop in a laminate film of stacked fine ceramic particulates. By this, the corrosion energy density of gold correlation is rarefied and diffused. After all, this brings about an improvement in corrosion resistance on the whole and exhibits excellent coating performance.
RAYDENT rust inhibiting performance
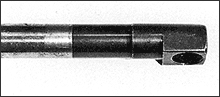
The RAYDENT coating exhibits a rust-inhibiting power that surpasses the technical concept of conventional JIS standards. For example, the part in the picture (floss holder) already shows wear on the coating, but has kept its rust-inhibiting state for as long as over 20 years.
RAYDENT coating performance on the raceway surface of a sliding portion
When subjected to surface pressure, the RAYDENT coating sheds its particulates in a certain amount (this is not exfoliation in the case of plating). However, the particulates get mixed in the white grease and, together with the grease, maintain their lubricating property. Therefore, there is no dry scattering or functional deterioration in cleanliness. Even after the coating has been removed, rust inhibition usually remains in effect on any of the various types of RAYDENT treatment surfaces for a long period of more than several years, as long as they are used in their original state.
As a result, the following results are available from RAYDENT treatment:
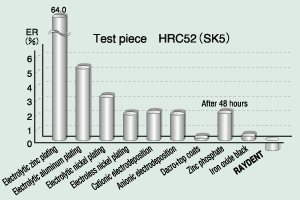
(1) The treatment never causes hydrogen embrittlement.
(2) The baking process after the treatment is omitted.
(3) An improvement in spring characteristics may be expected.
(4) Of the many surface treatment techniques, this rust-inhibiting method is most suitable for carbon steels and springs.
(5) It exhibits specific properties with regard to hydrogen ions.
* RAYDENT adhesion performance

The compound coating of RDT films (thermosetting fluorocarbon resin) will not crack, even for hairpin-shaped bending exceeding JIS.
Thus the RDT-improved compound coating never exfoliates and is dust-free in principle. Combined with its intrinsic high accuracy, it has been increasingly used in the area of semiconductor and liquid crystal equipment.
* Uses for wear resistance

Our fluorocarbon/graphite coating (2FGr)+RDT coating base brings about a result that is superior in its resistance to sliding wear to TiN (very hard film).
* Uses for corrosion resistance

Because of close adhesion, treated nuts and bolts keep their resilience and self-lubricating property to the limit of contact surface pressure. After fastening, a packing effect is brought about by the plastic deformation of the coating itself. Even if damage should occur under extreme pressure, the boundary layer between the RDT coating and the base forms a nearly perfect adhesion, which gives a strong rust-inhibiting effect to suppress the corrosion area against the corrosive action due to capillary intrusion through the gaps between threads.
 |
|---|
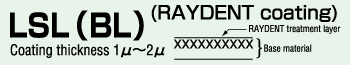 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
(SEAJ)
Supporting member of the Semiconductor Equipment Association of Japan
(SEMI)
Member of Smiconductor Equipment and Materials International
![]()
39-3, Enoguchi, Shimata, Kumiyama-cho, Kuse-gun, Kyoto, Japan 613-0043
【TEL】+81-75-631-5146
【FAX】+81-75-631-5147
【E-Mail】info@raydent.co.jp
【URL】https://raydent.co.jp
![]()
RAYDENT and raydent are registered treadmarks of RAYDENT INDUSTRIAL CO.,LTD.